上面我们完成了赫夫曼编码,我们来实现下解码。完成对压缩数据的解码。
/**
*
* @param huffmanCodes 赫夫曼编码表 map
* @param huffmanBytes 赫夫曼编码得到的字节数组
* @return 就是原来的字符串对应的数组
*/
private static byte[] decode(Map<Byte,String> huffmanCodes, byte[] huffmanBytes) {
//1. 先得到 huffmanBytes 对应的 二进制的字符串 , 形式 1010100010111...
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
//将byte数组转成二进制的字符串
for(int i = 0; i < huffmanBytes.length; i++) {
byte b = huffmanBytes[i];
//判断是不是最后一个字节
boolean flag = (i == huffmanBytes.length - 1);
stringBuilder.append(byteToBitString(!flag, b));
}
//把字符串安装指定的赫夫曼编码进行解码
//把赫夫曼编码表进行调换,因为反向查询 a->100 100->a
Map<String, Byte> map = new HashMap<String,Byte>();
for(Map.Entry<Byte, String> entry: huffmanCodes.entrySet()) {
map.put(entry.getValue(), entry.getKey());
}
//创建要给集合,存放byte
List<Byte> list = new ArrayList<>();
//i 可以理解成就是索引,扫描 stringBuilder
for(int i = 0; i < stringBuilder.length(); ) {
int count = 1; // 小的计数器
boolean flag = true;
Byte b = null;
while(flag) {
//1010100010111...
//递增的取出 key 1
String key = stringBuilder.substring(i, i+count);//i 不动,让count移动,指定匹配到一个字符
b = map.get(key);
if(b == null) {//说明没有匹配到
count++;
}else {
//匹配到
flag = false;
}
}
list.add(b);
i += count;//i 直接移动到 count
}
//当for循环结束后,我们list中就存放了所有的字符 "i like like like java do you like a java"
//把list 中的数据放入到byte[] 并返回
byte b[] = new byte[list.size()];
for(int i = 0;i < b.length; i++) {
b[i] = list.get(i);
}
return b;
}
/**
* 将一个byte 转成一个二进制的字符串, 如果看不懂,可以参考我讲的Java基础 二进制的原码,反码,补码
* @param b 传入的 byte
* @param flag 标志是否需要补高位如果是true ,表示需要补高位,如果是false表示不补, 如果是最后一个字节,无需补高位
* @return 是该b 对应的二进制的字符串,(注意是按补码返回)
*/
private static String byteToBitString(boolean flag, byte b) {
//使用变量保存 b
int temp = b; //将 b 转成 int
//如果是正数我们还存在补高位
if(flag) {
temp |= 256; //按位与 256 1 0000 0000 | 0000 0001 => 1 0000 0001
}
String str = Integer.toBinaryString(temp); //返回的是temp对应的二进制的补码
if(flag) {
return str.substring(str.length() - 8);
} else {
return str;
}
}
测试
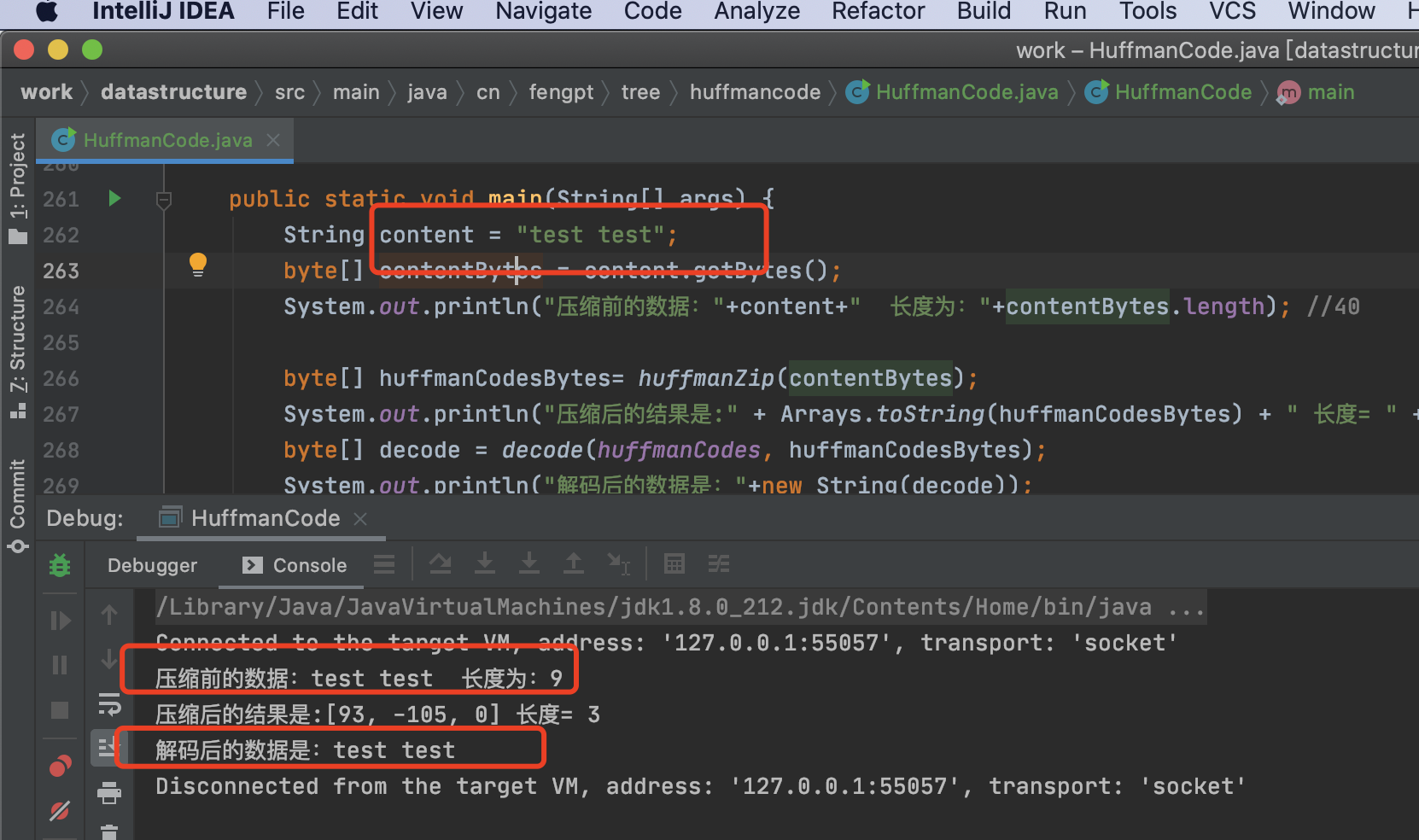
public static void main(String[] args) {
String content = "test test";
byte[] contentBytes = content.getBytes();
System.out.println("压缩前的数据:"+content+" 长度为:"+contentBytes.length); //40
byte[] huffmanCodesBytes= huffmanZip(contentBytes);
System.out.println("压缩后的结果是:" + Arrays.toString(huffmanCodesBytes) + " 长度= " + huffmanCodesBytes.length);
byte[] decode = decode(huffmanCodes, huffmanCodesBytes);
System.out.println("解码后的数据是:"+new String(decode));
}


评论区